|
|
- A genus of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that utilizes citrate as a sole carbon source. It is pathogenic for humans, causing enteric fevers, gastroenteritis, and bacteremia. Food poisoning is the most common clinical manifestation. Organisms within this genus are separated on the basis of antigenic characteristics, sugar fermentation patterns, and bacteriophage susceptibility.
(Source: National Library of Medicine 2013 MeSH Scope Note and Classification)
- Images
-
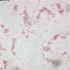
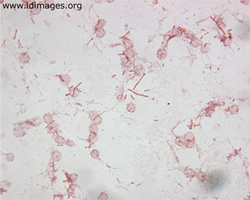 - Figure 1. Salmonella typhi, shown by gram stain of blood culture.

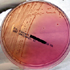
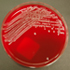
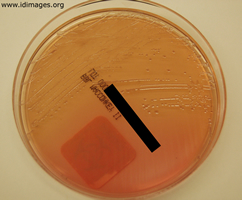 - Figure 2. Salmonella typhi, shown on MacConkey agar subculture.

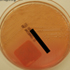
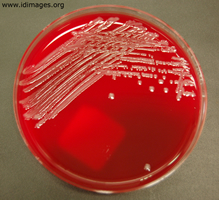 - Figure 3. Salmonella typhi shown on blood agar.

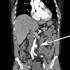
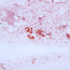
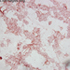
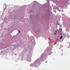
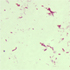
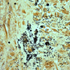
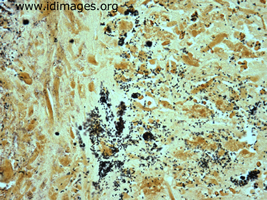 - Figure 4. Salmonella, group B, seen in Steiner stain of resected mycotic aneurysm.

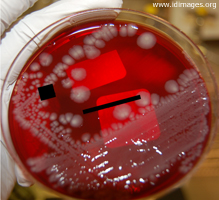 - Figure 5. Salmonella enterica serotype Heidelberg, on blood agar.

- Related Cases
- Related Images From Cases
-





- References
-
- National Library of Medicine 2013 MeSH Scope Note and Classification
|
|