- A genus of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria whose organisms arrange singly, in pairs, or short chains. This genus is commonly found in the intestinal tract and is an opportunistic pathogen that can give rise to bacteremia, pneumonia, urinary tract and several other types of human infection.
Source: National Library of Medicine 2013 MeSH Scope Note and Classification
- Images
-

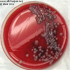
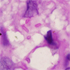
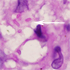
- Figure 1. Gram stain of Klebsiella pneumoniae ssp. rhinoscleromatis.

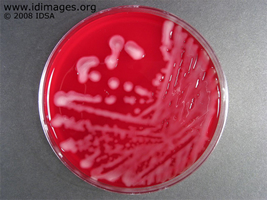
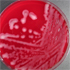
- Figure 2. Growth of Klebsiella on sheep blood agar.

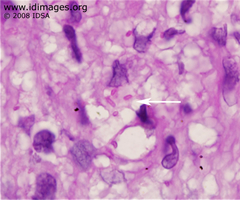
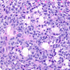
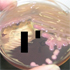
- Figure 3. Klebsiella pneumoniae ssp. rhinoscleromatis, PAS stain of epiglottis biopsy specimen.

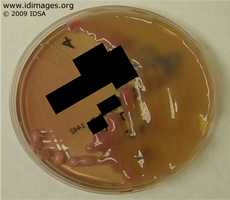
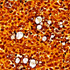
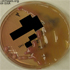
- Figure 4. Hypermucoviscous colonies of Klebsiella pneumoniae on MacConkey agar.


- Figure 5. String test with colony of Klebsiella pneumoniae.

- Notes
- For Figures 1, 2 and 3, please refer to the Contributing Authors page for the list of IDSA 2008 case contributors. These images and the related case were originally presented at the joint Annual Meeting of the Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC, 48th meeting) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2008 (IDSA, 46th meeting) during an interactive session on Fellows' Day. Copyright 46th Annual Meeting of Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA), 2008. Used with permission.
For Figures 4 and 5, please refer to the Contributing Authors page for the list of IDSA 2009 case contributors. This case was originally presented at the Annual Meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2009 (IDSA, 47th meeting) during an interactive session on Fellows' Day. Copyright 47th Annual Meeting of Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA), 2009. Used with permission.
- Related Cases
Show All Related Cases (7) »
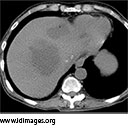
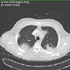
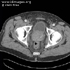
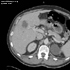
- Related Images From Cases
-



- References
-
- National Library of Medicine 2013 MeSH Scope Note and Classification